What is ornithine? It consists of a non-essential amino acid. Discover its benefits, what are its functions and the foods richest in ornithine.

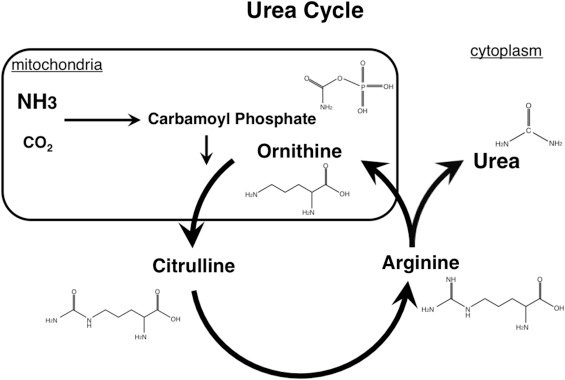
The ornithine is a nonessential amino acid that is part in the synthesis of arginine and it is a derivative of the glutamate, two essential amino acids for the health of our body. Although it is true that it tends to be less known than other non-essential amino acids.
In the case of amino acids, surely you know that they are divided into essential amino acids (those that can be provided to our body only from food), and non-essential amino acids (which can be synthesized, and we find them in our body).
What is ornithine?
It consists of a non-essential amino acid, which means that we find it in certain parts of our body, which can synthesize it without problems and it is not only necessary to provide it through food or daily diet.
It is part of the synthesis of arginine, and is also known as a derivative of glutamate (or glutamic acid).
Ornithine functions:
- Stimulates growth hormone.
- Improves our immune system and our defenses.
- Regenerates the liver.
- It influences the synthesis of insulin in the pancreas.
- Helps in the metabolisation of fats.
- Promotes tissue healing.
Health benefits of ornithine:
Ornithine is a non-essential amino acid that improves our body’s immune system, stimulating certain lymphocytes, which in turn helps improve our defenses.
Because it stimulates collagen synthesis, it promotes proper tissue healing. In addition, it helps in the regeneration of the liver, while participating in the synthesis of insulin in the pancreas.
On the other hand, it also stimulates growth hormone, and is usually linked to the metabolism of fats.
Where to find ornithine?
Here are the foods richest in ornithine:
- Food of animal origin: meat, fish, milk and eggs.
- Plant-based foods: legumes and sprouts.